Overview
Introduction to GraalVM
The biggest change brought by Spring Boot 3.0 this time is the support of GraalVM's native image, which is also the part that they spend more time and energy on as emphasized in the official document. As an alternative to JRE, GraalVM technology pre-compiles Java applications through technologies such as Ahead-Of-Time (AOT), allowing Spring to learn more about the application when it runs the application, making the entire application start faster. In addition, the final application can be smaller and occupy less memory by eliminating some unnecessary content during the compilation process through the compilation tool. It is very friendly to some scenarios that require very high startup speed, such as Serverless and FaaS scenarios! This time, Spring Boot 3.0 directly migrated it from Spring Native to Spring Boot, which also indicates that the technology has gradually matured, and the Spring ecosystem has entered the GraalVM stage!
Compared with the JVM compilation and deployment method, GraalVM has the following characteristics:
- In the application construction phase, static analysis of the application starts from the main entry point.
- When creating a native image, through code analysis, the inaccessible code will be deleted and will not become part of the executable file, so the package size can be compressed to a certain extent.
- GraalVM cannot directly perceive the dynamic elements of the code. Therefore, for applications with reflection, serialization, and dynamic proxies, you need to provide relevant hint configuration files in advance to help analyze the application. For related operations, please refer to official documents.
- The application classpath is fixed at build time and cannot be changed.
- Without lazy class loading, everything in the executable will be loaded into memory on startup.
- The supported Java applications have some restrictions in some aspects, so there is currently no guarantee that all previous Java applications can be directly built using GraalVM technology, and there may be incompatibility exceptions with a certain probability.
Some middleware clients included in the Spring Cloud Alibaba 2022.0.0.0 version released this time have completed the adaptation for building GraalVM native applications. The following are examples of applications related to the currently supported service registration and discovery modules that are being upgraded to Spring by the community. After Boot 3.0, use GraalVM to build a native application image to do tests related to startup speed and runtime occupancy content(The following test process is simulated 3 times under macOS 11.4, 2.6 GHz 6-Core Intel Core i7 processor, and 16G memory environment measured by taking the average value):
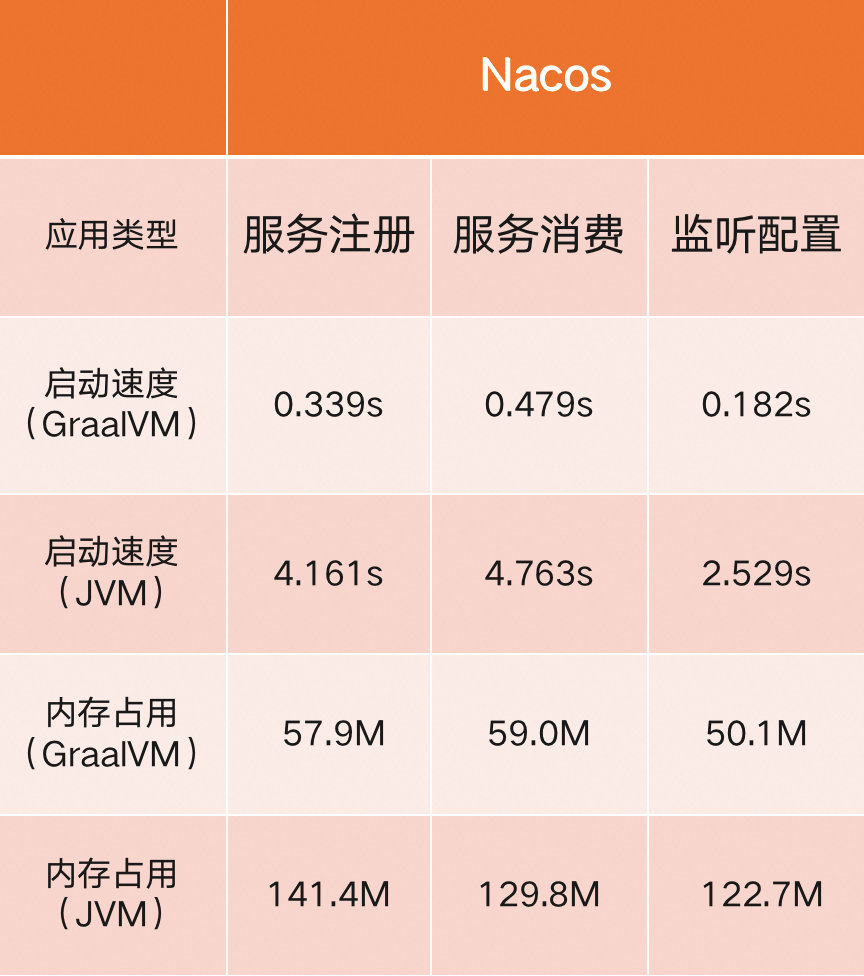
From the above comparison, it can be found that the latest GraalVM-based Spring Cloud Alibaba application that supports Spring Boot 3.0 will be greatly reduced in terms of startup speed, runtime memory usage, and application package size. For example, the startup speed of service registration consumer applications has increased by nearly 10 times, the runtime memory usage is reduced by nearly 2/3 compared to the original, the effect is very obvious. This brings significant advantages to applications hosted on the cloud in the cloud-native era, allowing them to perform elastic expansion and contraction faster and reduce the overall cost of using the cloud for enterprises!